Cheese is a delicious and versatile food enjoyed worldwide, whether melted on pizza, grilled in sandwiches, or baked into casseroles. But many people wonder: does cheese lose protein when heated? Protein is essential for muscle growth, repair, and overall health, making it crucial to understand how cooking affects it. In this article, we’ll dive into the science behind heating cheese, how it impacts protein structure, and whether cooking affects its nutritional value.
Understanding Cheese and Its Protein Content
What Makes Cheese a Good Source of Protein?
Cheese is widely recognized as a rich source of protein, particularly casein protein, which is slow-digesting and highly beneficial for muscle maintenance and growth. Here’s why cheese is a great protein source:
- Casein Dominance: Unlike whey protein, which digests quickly, casein proteins in cheese break down slowly, providing a steady supply of amino acids.
- Amino Acid Profile: Cheese contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein—necessary for muscle repair, immune function, and overall health.
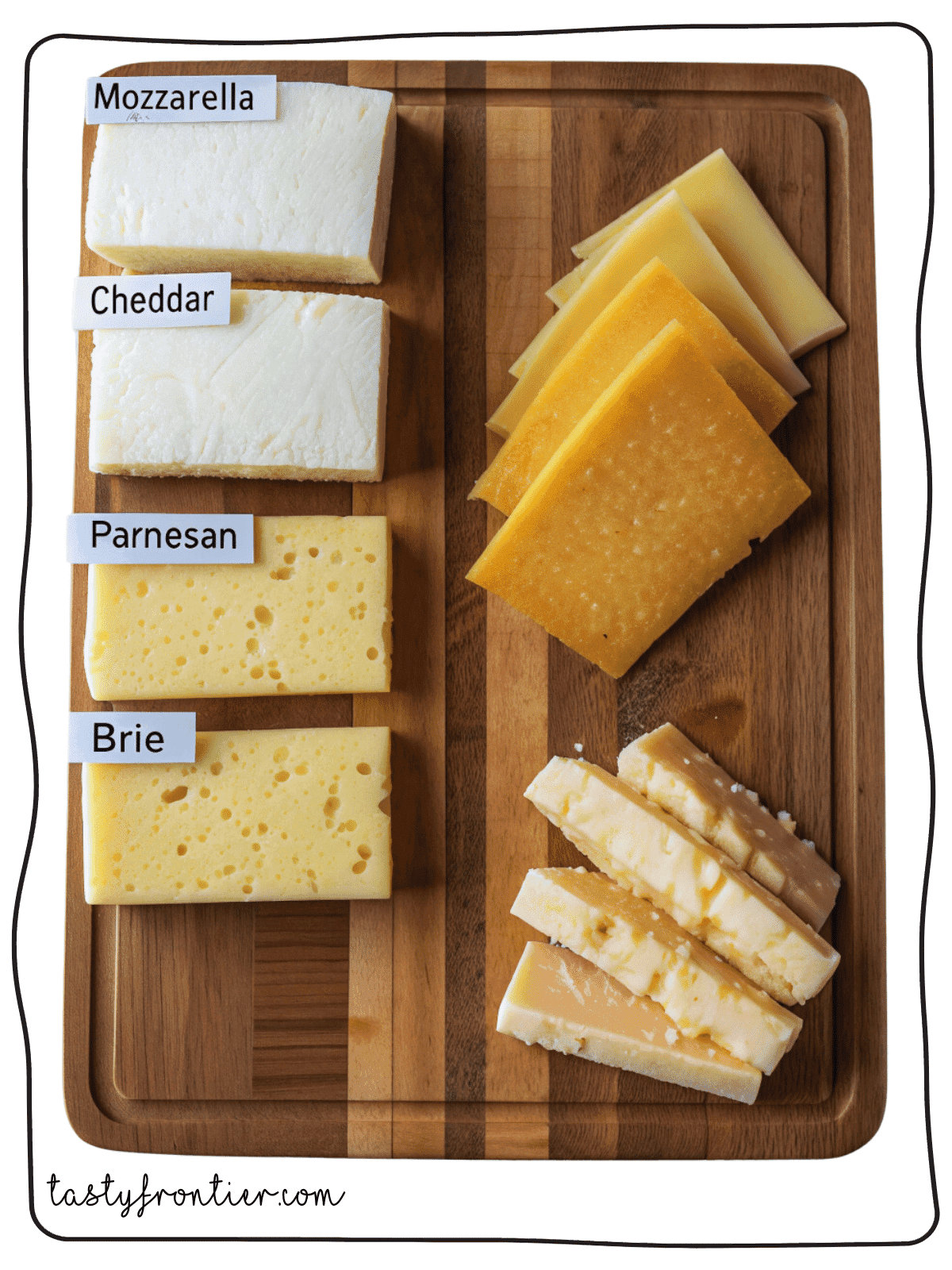
- High Protein Density: Hard cheeses, like Parmesan and Cheddar, contain more protein per gram compared to softer varieties like Brie or Ricotta.
Protein Content in Popular Cheeses (Per 100g)
| Cheese Type | Protein Content (g) |
|---|---|
| Parmesan | 35g |
| Cheddar | 25g |
| Mozzarella | 22g |
| Feta | 14g |
| Brie | 10g |
The harder and drier the cheese, the more protein it contains due to its lower moisture content.
Why Does Cheese React Differently to Heat?
Not all cheeses behave the same when heated. Their reaction depends on moisture, Fat, and protein composition.
- Hard cheeses (Parmesan, Cheddar, and Gouda) tend to crisp up when heated because of their low moisture content.
- Retain their shape, but may become slightly oily.
- Semi-soft cheeses (Mozzarella, Provolone, Monterey Jack)Become stretchy and gooey due to casein proteins forming long strands.
- High moisture content allows easy Melting.
- Soft cheeses (brie, camembert, feta, and goat cheese) can be made creamy and spreadable but stretch a little.
- It may separate slightly due to its high-fat content.
- Processed Cheeses (American Cheese, Cheese Sauce)Melt smoothly due to emulsifiers and stabilizers.
- Often contain added fats and preservatives, which affect nutritional value.
How Does Cheese Structure Affect Its Heat Sensitivity?
Cheese is made up of three primary components:
- Protein (Casein): Forms the structure and determines Texture.
- Fat: Affects mouthfeel and melting behavior.
- Moisture: Plays a crucial role in stretchiness and spreadability.
When heated, the protein matrix breaks down, allowing Fat and moisture to flow. This is why some cheeses melt smoothly while others become stringy or separate.
1️⃣ “1-Ingredient Keto Cottage Cheese Chips – High Protein Snack Delight”
👉 Looking for a high-protein cheese snack? Check out this recipe for crispy cottage cheese chips!
🔗 Read Here
Does Heating Cheese Reduce Its Protein Content?
Does Heat Destroy Protein in Cheese?
Many worry that cooking cheese could destroy its protein content, making it less nutritious. However, heat does not eliminate protein; it changes its structure through denaturation.
What is Protein Denaturation?
Denaturation occurs when heat, acid, or mechanical force alters the shape of a protein’s molecules. This process:
- Unfolds protein structures, making them easier to digest.
- Does not remove or destroy protein, meaning the nutritional value remains intact.
- Affects Texture, which is why melted cheese feels different from cold cheese.
For example, when you melt Mozzarella on pizza or grill a cheese sandwich, the protein remains the same, but its structure changes.
Does Protein Go Away When Cheese is Heated?
No, heating cheese does not remove protein. The total amount of protein stays the same whether the cheese is raw or cooked. However, heating can impact:
1. Digestibility
- Denatured protein is often easier to digest because heat breaks down complex protein structures.
- Some people with mild dairy sensitivities may find cooked cheese easier to tolerate.
2. Texture and Appearance
- When heated, proteins in cheese break down and release fat and moisture, which is why some cheeses become oily or rubbery after excessive heating.
- Hard cheeses like Parmesan crisp up instead of melting due to low humidity.
3. Nutrient Stability
- Protein remains stable, but heat-sensitive vitamins like B12 may degrade at high temperatures.
- Minerals like calcium remain intact, ensuring you still get essential nutrients.
Does Reheating Cheese Affect Its Nutritional Value?
Reheating cheese multiple times does not reduce protein, but it can change:
- Moisture content: The more you heat cheese, the drier it becomes.
- Fat separation: Reheating causes Fat to break away from the protein, affecting Texture.
- Stretchiness: Some cheeses become less stretchy after reheating due to continued protein breakdown.
For best results, heat cheese only once and avoid overheating to maintain its ideal Texture and flavor
The Science Behind Heating Cheese and Protein Denaturation
What Happens to Cheese Proteins When Heated?
When cheese is heated, its protein structure changes due to denaturation. This process:
- Unfolds protein molecules, changing their Texture.
- Does not destroy protein, meaning you still get the same nutritional benefits.
- Affects Melting and stretchiness, depending on the type of cheese.
How Heat Alters Cheese Proteins
Cheese proteins (mainly casein) are arranged in a dense fat and moisture network. When heat is applied:
- Low heat (below 90°F or 32°C): Cheese softens as Fat begins to liquefy.
- Medium heat (90–150°F or 32–65°C): Proteins loosen, and the cheese begins to stretch (ideal for melted cheese dishes).
- High heat (above 150°F or 65°C): Proteins break down further, releasing fat and moisture, making the cheese greasy or rubbery.
This explains why Mozzarella becomes stretchy while Cheddar may turn oily when overheated.
Does Denatured Protein Still Provide Nutrients?
Yes! Even though denatured protein changes shape, it still provides the same essential amino acids. The body absorbs and utilizes denatured protein, just like raw protein.
Denatured Protein vs. Undenatured Protein
| Feature | Denatured Protein (Cooked Cheese) | Undenatured Protein (Raw Cheese) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Unfolded, easier to digest | Intact, harder to digest |
| Nutritional Value | Same protein content | Same protein content |
| Taste & Texture | Melted, soft, or crispy | Firm, chewy, or creamy |
| Digestibility | Often easier to digest | Can be harder for some people |
This means cooked cheese remains as nutritious as raw cheese but may feel different when eaten.
Why Does Some Cheese Stretch While Others Crisp Up?
The way cheese melts depends on protein composition, moisture content, and fat levels:
- Stretchy cheeses (Mozzarella, Provolone, and Gouda) contain high moisture and elastic protein bonds.
- When heated, proteins separate slightly but remain connected, creating a stretch effect.
- Crispy cheeses (Parmesan, Cheddar, and Romano) have low moisture and high protein density.
- Instead of stretching, they harden and crisp up when exposed to high heat.
- Soft, Non-Stretchy Cheeses (Brie, Camembert, Feta)Have high Fat and moisture but less structured protein networks.
- They melt into a creamy consistency rather than stretching.
This explains why Mozzarella on pizza forms long, stretchy strands, while Parmesan forms crispy cheese chips when baked.
Nutrient Loss in Heated Cheese
Does Cheese Lose Nutrients When Cooked?
While cheese retains its protein content when heated, high temperatures may affect other nutrients. The main components to consider are:
- Protein – Stays the same, only its structure changes (denaturation).
- Fats – Can separate and release oil but remain intact.
- Calcium & Minerals – Not affected by heat.
- Vitamins – Some heat-sensitive vitamins, like B12, may degrade.
Which Nutrients Are Most Affected by Heat?
| Nutrient | Effect of Heat |
|---|---|
| Protein | No loss, only structural changes |
| Calcium | Stable, not affected |
| Fat | May separate but remains intact |
| Vitamin B12 | Some loss at high heat (above 250°F/120°C) |
| Vitamin A & D | Mostly stable, minor loss at very high temperatures |
Does Reheating Cheese Affect Its Nutritional Value?
Reheating cheese multiple times may cause moisture loss and fat separation, but it does not reduce protein or minerals. However:
- Some water-soluble vitamins (like B vitamins) may degrade.
- Cheese may become less creamy and more rubbery after repeated heating.
To preserve nutrients, it’s best to melt cheese at lower temperatures and avoid excessive reheating.
How to Minimize Nutrient Loss When Cooking Cheese
To keep cheese as nutritious as possible, follow these tips:
✅ Use lower heat (below 250°F/120°C) when melting cheese.
✅ Limit reheating to prevent excessive fat separation.
✅ Combine cheese with vegetables to balance nutrition.
✅ Choose nutrient-rich cheeses (e.g., aged cheeses contain more calcium).
How Different Cheeses React to Heat
Not all cheeses respond to heat the same way. Their reaction depends on moisture content, fat percentage, and protein structure. Some cheeses melt beautifully, while others crisp up or become oily. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right cheese for cooking.
Do Some Cheeses Retain Protein Better Than Others?
Since heating doesn’t reduce protein content, all cheeses retain their protein value when cooked. However, moisture and fat levels influence how cheese reacts to heat.
How Cheese Type Affects Heat Reaction
| Cheese Type | Moisture Content | Melting Behavior | Best Use in Cooking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mozzarella | High (50-60%) | Stretchy & gooey | Pizza, pasta, grilled cheese |
| Cheddar | Medium (35-40%) | Melts smoothly but may get oily | Burgers, mac & cheese |
| Parmesan | Low (25-30%) | Crisps up instead of melting | Toppings, crisps |
| Feta | High (55-60%) | Softens but doesn’t melt | Salads, baking |
| Brie/Camembert | High (50-55%) | Becomes creamy | Baked dishes |
Why Some Cheeses Stretch While Others Crisp
- Stretchy cheeses (e.g., Mozzarella, Provolone) have elastic casein proteins that allow long strands to form.
- Crispy cheeses (e.g., Parmesan, Romano) have low moisture and dense proteins, causing them to harden rather than stretch.
- Soft cheeses (e.g., Brie, Feta) have high Fat and moisture but weak protein networks, making them creamy rather than stringy.
Why Does Cheese Become Stretchy or Gooey When Heated?
The casein protein network in cheese determines its melting behavior.
- Mozzarella & Provolone: Casein proteins form long, flexible chains, creating stretchiness.
- Cheddar & Gouda: Medium protein density makes them melt smoothly but not as stretchy.
- Brie & Camembert: High-fat content makes them creamy rather than stringy.
- Parmesan & Romano: Low moisture and tight protein bonds prevent Melting, leading to crispiness.
How Heat Affects Cheese Texture
| Temperature | Effect on Cheese |
|---|---|
| 90°F (32°C) | Softens slightly, fat begins to release |
| 130°F (55°C) | Melting begins, proteins loosen |
| 150°F (65°C) | Ideal stretch and gooey texture |
| 180°F (82°C) | Fat separates, cheese may become greasy |
| 200°F+ (93°C+) | Overheated cheese turns rubbery or crispy |
Does the Type of Cheese Affect How It Responds to Heat?
Yes! The Fat, moisture, and protein balance in cheese determines whether it will:
- Melt into a smooth, creamy consistency (like Brie or Cheddar).
- Stretch into long strands (like Mozzarella).
- Become crispy instead of melting (like Parmesan).
This is why choosing the right cheese for cooking is essential—not all cheeses work well for all recipes!
Is Cooked Cheese Less Healthy?
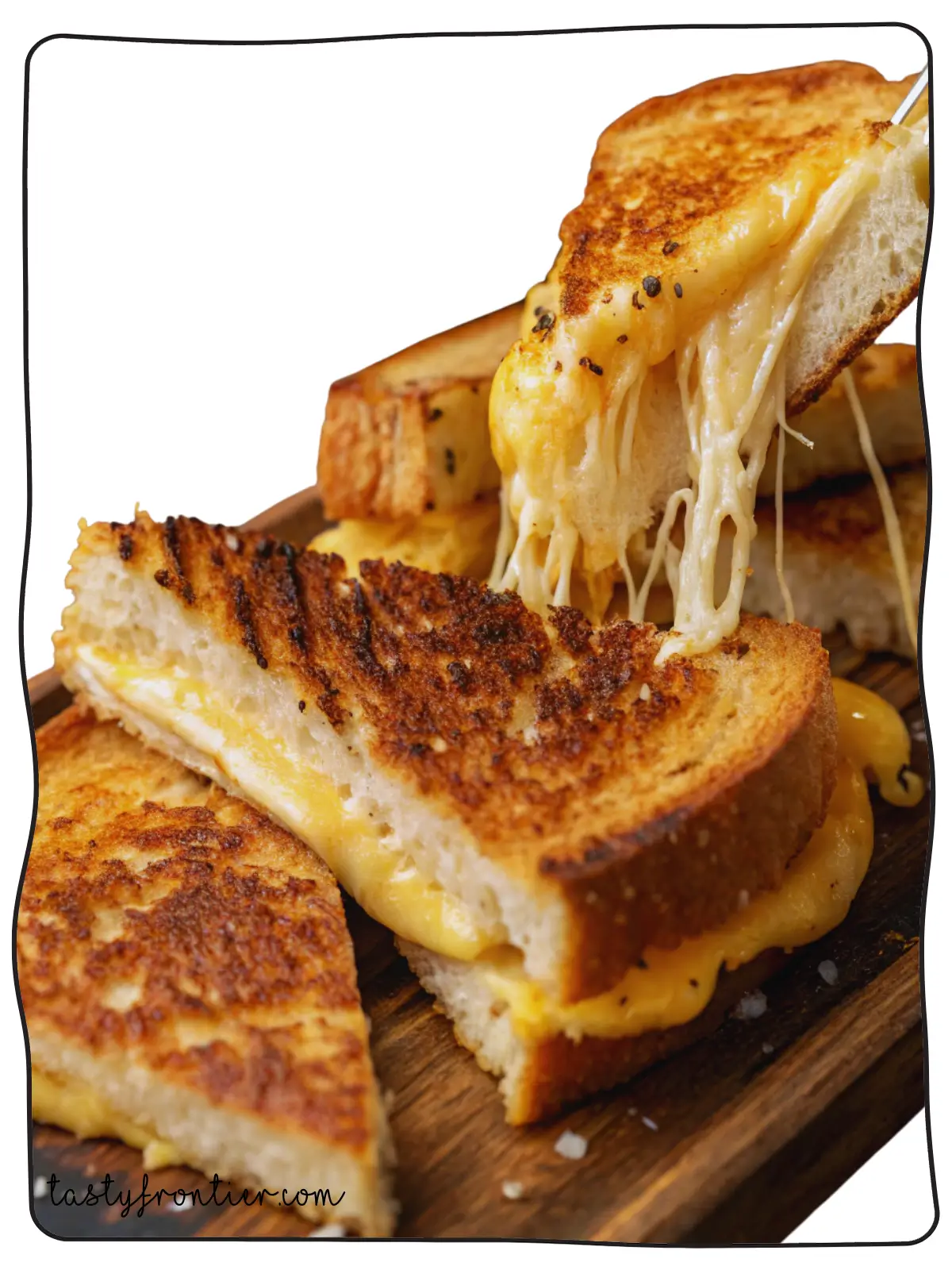

Many people wonder if cooking cheese makes it unhealthy. While heating cheese can alter its Texture and composition, it does not necessarily make it bad for you. However, added ingredients, high temperatures, and portion sizes can impact its overall health effects.
Does Cooking Cheese Make It Unhealthy?
The nutritional value of cheese remains the same after cooking, but some factors can affect its healthiness:
1. Fat Content and Oil Separation
- Cheese contains natural fats, which may separate when heated at high temperatures.
- This can create an oily texture, but the Fat is not lost or altered.
- Excessive heating can cause the cheese to release more oil, making dishes more Fat than intended.
2. Sodium and Preservatives
- Processed cheeses (like American cheese) often contain high sodium levels and preservatives.
- Cooking processed cheese may not significantly affect sodium content, but consuming large amounts can increase blood pressure risks.
3. Potential Acrylamide Formation
- Acrylamide is a compound that forms when high-carb foods are exposed to high heat (above 248°F or 120°C).
- Cheese is low in carbohydrates, meaning it does not form acrylamide easily.
- However, dishes containing bread, crackers, or potatoes with cheese (e.g., grilled cheese, nachos) may form small amounts.
4. Vitamin Loss
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) remain stable, even at high heat.
- Water-soluble vitamins (like B12) may degrade slightly at temperatures above 250°F (120°C).
Are There Healthier Ways to Cook Cheese?
To enjoy cheese more healthily, consider these tips:
✅ Use lower temperatures to melt cheese instead of high-heat frying or broiling.
✅ Pair cheese with fiber-rich foods (like vegetables and whole grains) to balance fat intake.
✅ Choose natural, aged cheeses over processed varieties with added preservatives.
✅ Limit additional fats (like butter or oil) when cooking with cheese.
Does the Cooking Method Matter?
Yes! How you cook cheese can impact its healthiness and Texture.
| Cooking Method | Effect on Cheese | Health Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Baking (Oven) | Melts evenly, enhances flavor | Retains nutrients, but may lose moisture |
| Grilling (Pan, BBQ) | Creates crispy edges, melts inside | Can lead to oil separation, but maintains nutrients |
| Frying (Deep-Fried Cheese) | Crispy and golden | Adds extra fat, can reduce nutrient density |
| Microwaving | Quick melting | Retains nutrients but may become rubbery |
For healthier cheese dishes, opt for baking or light grilling instead of deep-frying.
2️⃣ “Seafood Mac and Cheese Recipe”
👉 Discover how melted cheese works in creamy mac and cheese dishes.
🔗 Read Here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This section will answer the most common questions about whether cheese loses protein when heated and how cooking affects its nutritional value.
1. Does Reheating Cheese Affect Its Protein Content?
No, reheating cheese does not reduce its protein content. The total amount of protein remains the same before and after heating. However, reheating can change its Texture, making it drier, greasier, or rubbery.
To avoid texture loss, reheat cheese at a lower temperature and prevent overheating.
2. Can Cooking Cheese Make It Unhealthy?
Not necessarily. Cooking cheese does not make it unhealthy; factors like high heat, added fats, and processed ingredients can impact its nutritional quality.
Natural cheeses (Cheddar, Mozzarella, Parmesan) are still healthy after heating.
Processed cheeses (American cheese, cheese sauces) often contain extra sodium, preservatives, and fats that may be less healthy.
Healthier Cooking Options:
✅ Use low to medium heat to prevent excessive fat separation.
✅ Choose natural cheeses over processed varieties.
✅ Avoid deep-frying cheese, as it adds unnecessary fats.
3. Does the Type of Cheese Affect How It Responds to Heat?
Yes! Different cheeses melt, stretch, or crisp up based on moisture, Fat, and protein content.
Mozzarella & Provolone → Stretchy when heated.
Cheddar & Gouda → Melts smoothly but may get oily.
Parmesan & Romano → Crisps up instead of melting.
Brie & Camembert → Becomes soft and creamy.
4. Is Protein Destroyed by Heating?
No, protein is not destroyed by heating. Instead, it undergoes denaturation, where the protein structure changes but retains its nutritional value. The body still absorbs and uses denatured proteins for muscle growth and repair.
5. Does Cheese Lose Nutrients When Heated?
Protein and calcium stay the same.
Some vitamins (like B12) may degrade slightly at high heat.
Fat can separate but does not disappear.
To preserve nutrients, cook cheese at moderate temperatures and avoid excessive reheating.
6. How Does Heat Affect Protein in Cheese?
Low heat → Softens cheese, no major changes.
Medium heat → Melts cheese, making it stretchier.
High heat → May cause fat separation, making cheese greasy or crispy.
Regardless of temperature, protein remains intact and beneficial.
7. Does Protein Go Away When Heated?
No, protein does not disappear when cheese is heated. It may denature, but the amount of protein remains the same.
For example:
100g of raw Cheddar = 25g protein
100g of melted Cheddar = 25g protein
8. Does Heating Cheese Reduce Protein?
No, heating cheese does not reduce protein. The nutritional value remains unchanged, but heat can change cheese’s Texture and structure.
What Can Change?
❌ Protein structure (denaturation)
❌ Texture (cheese becomes stretchier, creamier, or crispier)
✅ Total protein content stays the same
9. Why Does Cheese Become Stretchy or Gooey When Heated?
This happens because casein proteins form a network that holds fat and moisture. When heated:
Casein proteins loosen, allowing the cheese to stretch.
Fat and moisture move freely, creating a gooey texture.
This effect is strongest in Mozzarella, Provolone, and Gouda, which have the right moisture, Fat, and protein balance.
10. Does Reheating Cheese Affect Its Protein Content?
No, reheating cheese does not reduce protein content. However, multiple reheatings can make cheese tougher and drier, affecting how it feels when eaten.
Best Practice:
✅ Reheat cheese gently at a lower temperature to maintain Texture and flavor.

Final Thoughts & Conclusion
After exploring the effects of heat on cheese, it’s clear that cheese does not lose protein when heated. While heating can change its Texture, structure, and moisture content, the nutritional value of protein remains intact. Here’s a recap of the key points we’ve covered:
Does Cheese Lose Protein When Heated? The Final Answer
✅ No, heating cheese does not reduce its protein content. The protein structure may change (denaturation), but the total protein amount remains the same.
✅ Different cheeses react differently to heat based on their moisture, Fat, and protein content. Some stretch (like Mozzarella), while others crisp up (like Parmesan).
✅ Nutrient loss is minimal—while some vitamins (like B12) may degrade at very high temperatures, protein, calcium, and fats remain stable.
✅ Reheating cheese multiple times can affect Texture but does not remove protein.
✅ The cooking method matters—baking and grilling preserve nutrients better than frying or overheating.
How to Maximize the Nutritional Benefits of Cheese
To get the most health benefits from cooked cheese, follow these simple tips:
🔥 Use low to moderate heat – High temperatures can change Texture and cause excessive oil separation.
🧀 Choose natural cheeses – Avoid processed varieties with high sodium and additives.
🥗 Pair cheese with nutrient-rich foods – Combining cheese with whole grains and vegetables enhances its nutritional profile.
♨️ Limit reheating – Reheat cheese at low temperatures to preserve its Texture and avoid excessive drying.
Who Should Be Concerned About Heating Cheese?
Most people can enjoy cooked cheese without worry, but some individuals might need to be mindful:
- People with lactose intolerance – Cooking does not remove lactose, but aged cheeses (like Parmesan) have lower lactose levels.
- Those watching fat intake – Cooking cheese does not increase fat, but excessive heating can release oils, making dishes appear greasier.
- People on low-sodium diets – Processed cheeses often contain more sodium, so opt for natural, lower-sodium cheeses.
Final Verdict: Should You Worry About Heating Cheese?
Not! Heating cheese does not destroy its protein or make it significantly less nutritious. Cheese remains a valuable source of protein, calcium, and essential nutrients, whether raw or cooked. Cheese remains a delicious and healthy addition to any diet as long as it’s consumed in moderation and cooked properly.











2 thoughts on “Does Cheese Lose Protein When Heated?”
Comments are closed.